As environmental concerns escalate, the demand for sustainable products has never been more pressing. Traditional manufacturing practices often rely on non-renewable resources, contributing to pollution, waste, and the depletion of natural reserves. However, a wave of innovation is reshaping this paradigm, introducing environmentally friendly materials that are both functional and scalable. This article explores cutting-edge sustainable materials that pave the way for a greener future.
1. Biodegradable Plastics:
Plastic pollution has become a global crisis. While traditional plastics can persist for centuries, biodegradable alternatives offer a more sustainable solution.
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): Derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, PLA is biodegradable and widely used in packaging, disposable utensils, and medical implants. Coca-Cola’s PlantBottle, made partially from PLA, is a prime example of this innovation.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Produced by bacterial fermentation, PHA is another biodegradable polymer degrading in marine and soil environments. Danimer Scientific uses PHA to create compostable straws, reducing ocean-bound plastic pollution.
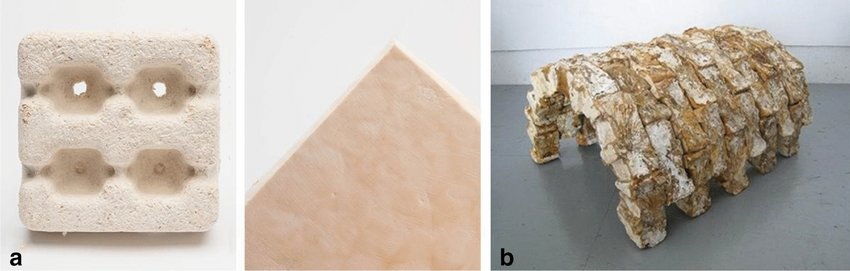
2. Mushroom-Based Materials:
Mushrooms, or mycelium (the root structure of fungi), are emerging as a highly sustainable material with applications in packaging, construction, and design.
- Mycelium Packaging: Mycelium can be grown into custom molds, offering a biodegradable alternative to Styrofoam. Companies like IKEA and Dell have experimented with mycelium packaging for electronics and furniture.
- Mycelium in Construction: Mycelium can also be used as a building material, offering a lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly option. Ecovative Design has developed mycelium-based panels for furniture and construction.
3. Recycled Materials:
Recycling plays a crucial role in reducing waste and conserving resources. Advances in recycling technology have expanded the range of materials that can be reused.
- Recycled PET (rPET): Derived from used plastic bottles, rPET is used in new bottles, textiles, and packaging. Adidas’ partnership with Parley for the Oceans to create footwear from ocean plastic is a notable example.
- Recycled Metals: Aluminum and steel are highly recyclable metals that can be reused to produce new products, reducing the need for mining and energy consumption. Apple’s commitment to using 100% recycled aluminum in its MacBook line is a testament to this approach.

4. Plant-Based Alternatives:
Plant-based materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional products.
- Bamboo: Bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource used in textiles, kitchenware, and other products. Bamblu, a sustainable bedding brand, uses bamboo fibers to create eco-friendly sheets.
- Hemp: Hemp is a versatile crop that can be used for textiles, building materials, and bioplastics. Pangaia, a sustainable clothing brand, uses hemp and seaweed-based fibers for its garments.

5. Graphene:
Graphene, a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms, is renowned for its strength, conductivity, and lightweight properties. While not inherently biodegradable, its efficiency in various applications makes it a promising sustainable material.
- Energy Efficiency: Graphene is used in solar panels and batteries, improving energy efficiency and reducing the need for frequent replacements. Samsung is investing in graphene technology for smartphone batteries.
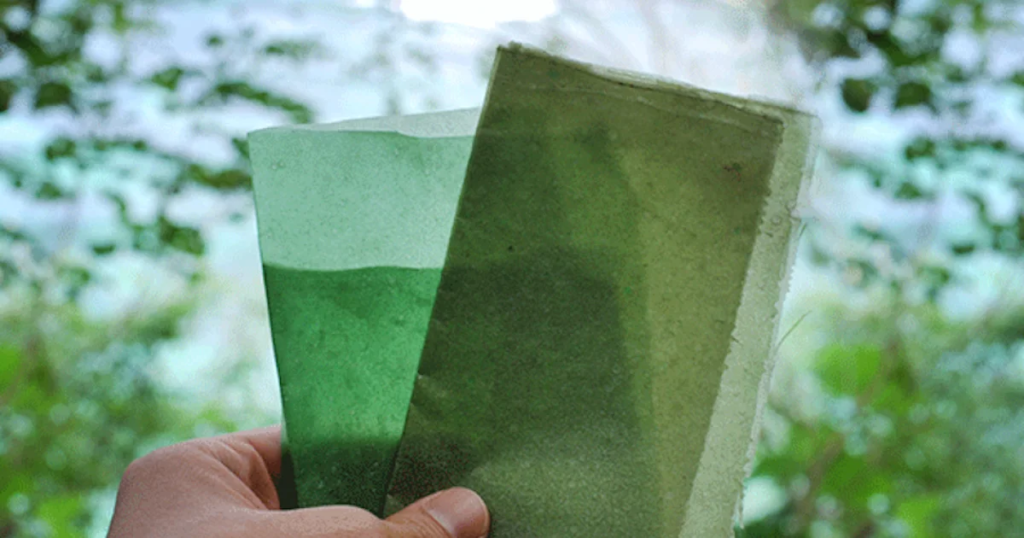
6. Seaweed-Based Packaging:
Seaweed is emerging as a sustainable alternative for packaging, offering biodegradable and often edible solutions.
- Seaweed Packaging: Notpla, a London-based startup, has developed edible water capsules made from seaweed, providing a zero-waste solution for single-use packaging.

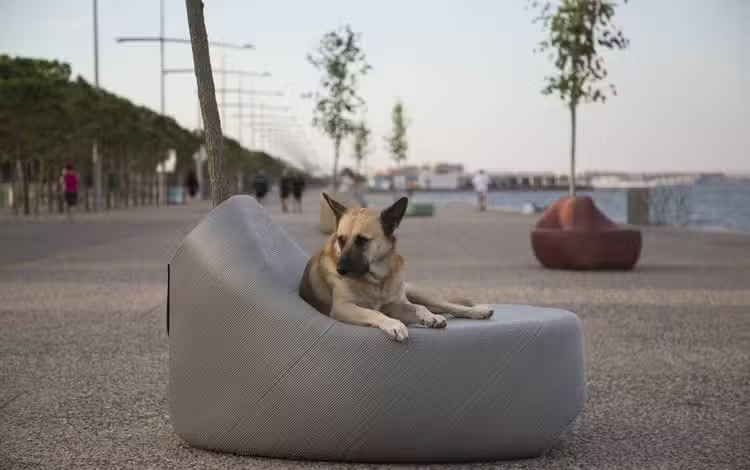
7. 3D-Printed Sustainable Materials:
3D printing technology allows for precise product creation, reducing material waste. Sustainable materials, like bioplastics and recycled filament, can be used in 3D printing to enhance sustainability.
Recycled Filament: The New Raw uses 3D printing to turn plastic waste into public furniture, demonstrating the potential for large-scale applications of recycled materials.

Conclusion
Sustainable product design and material innovation are crucial for addressing environmental challenges. By incorporating sustainable materials into their operations, businesses can reduce their environmental impact and meet the growing demand for responsible consumption. 1 As consumers and industries embrace these innovations, the future of product design is shaped by a commitment to sustainability, driving us toward a more resource-efficient and environmentally conscious world.






