Cisco Systems, a global leader in networking and digital communications, has embedded sustainability into its core strategy, recognizing that its technological innovation must align with environmental stewardship, social equity, and long-term economic viability. The company’s approach to sustainability addresses both its operational footprint and the broader enabling role of its products in helping other organizations reduce their carbon impact.
Cisco’s FY2023 Purpose Report outlines ambitious targets aligned with frameworks like the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through initiatives spanning circular product design, energy-efficient technology, digital inclusion, and responsible sourcing, Cisco is positioning itself as a sustainability leader in the tech sector.
Sustainability Strategy and Goals
Cisco’s sustainability roadmap is driven by three central themes: Net Zero Commitment, Circular Economy Design, and Inclusive Digital Infrastructure. These strategies are closely aligned with the UN SDGs, particularly SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Net Zero and Carbon Emissions
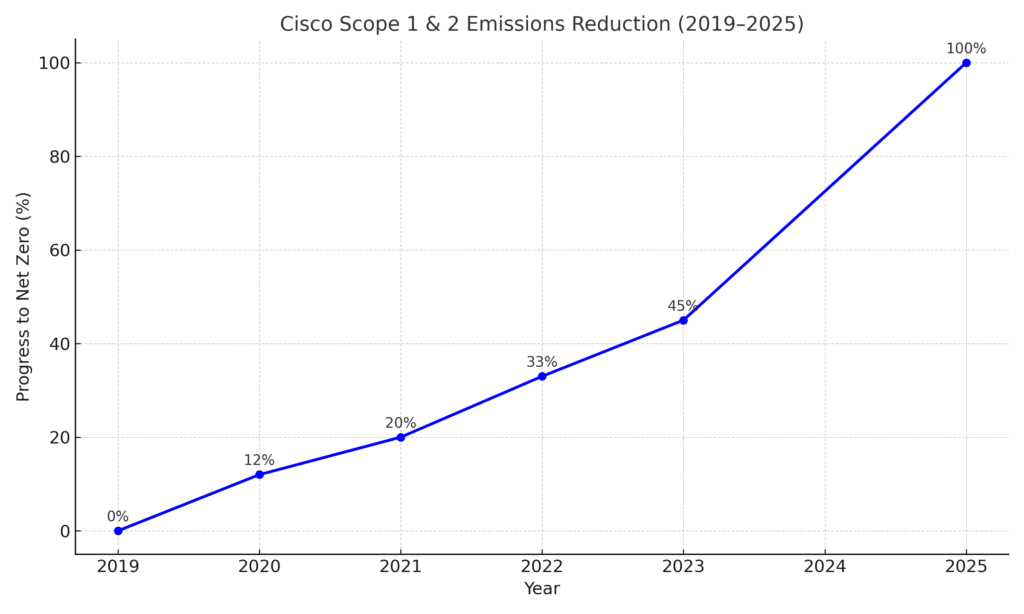
Cisco has committed to achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions across its entire value chain (Scopes 1, 2, and 3) by 2040. The company’s interim targets include:
- Net zero for global Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 2025
- 30% reduction in Scope 3 emissions from use of sold products by 2030
Cisco has already transitioned 85% of its global electricity use to renewable sources, and aims to reach 100% renewable energy in all global operations by 2025.
Water Stewardship
Though not a high-water-use industry, Cisco has committed to improving water use efficiency in its data centers and offices. It reports that 92% of water withdrawn in 2023 was returned to the source without significant contamination.
Regenerative Practices and Biodiversity
Cisco’s direct involvement in regenerative agriculture is minimal, but the company supports biodiversity indirectly through responsible supplier management and limiting the sourcing of conflict minerals. It works with the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) to ensure traceable and ethical sourcing.
Packaging and Circular Economy
Circularity is at the heart of Cisco’s product lifecycle approach. The company has committed to designing all new products and packaging for circularity by FY2025.
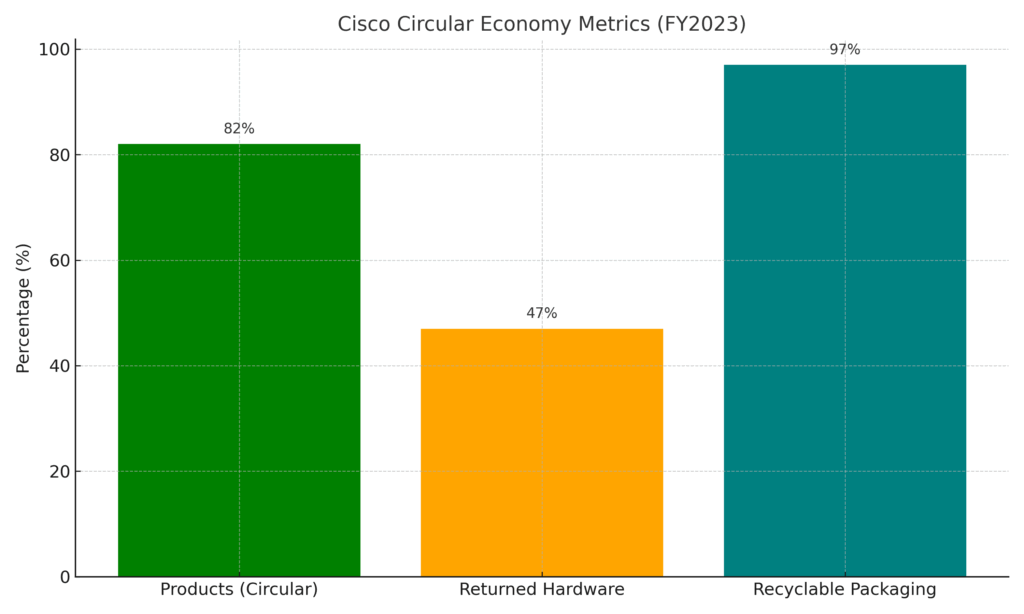
- As of 2023, 47% of Cisco’s hardware products were returned via take-back and reuse programs.
- 82% of Cisco products shipped in FY2023 met circular design principles.
Cisco’s packaging also reflects sustainability commitments:
- 97% of product packaging is recyclable or compostable.
- Transitioned to plastic-free packaging in key product lines, including Webex devices.
Human Rights and Responsible Sourcing
Cisco maintains one of the tech industry’s most rigorous supply chain responsibility programs, with annual audits covering 96% of manufacturing spend. Key focuses include:
- Ethical labor practices
- Worker health and safety
- Conflict-free mineral sourcing
- Transparent reporting through CDP and EcoVadis platforms
Digital Inclusion and Equity
Through its Cisco Networking Academy, the company has trained over 20 million people globally since 1997, including many in underserved communities. In FY2023 alone, Cisco helped 3.2 million learners advance digital skills.
Governance and Transparency
Cisco’s ESG efforts are overseen by a dedicated ESG Steering Committee reporting directly to the board. The company has adopted the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) frameworks to ensure robust reporting and stakeholder engagement.
Technology and Innovation
Cisco’s core business—enabling global digital connectivity—plays a critical role in decarbonization. Key innovations include:
- Energy-efficient networking equipment: reducing energy intensity by 40% per unit of bandwidth since 2015.
- Silicon One chipset platform: improves performance and power efficiency, reducing emissions from high-performance computing infrastructure.
Global Partnerships and Advocacy
Cisco is a founding member of the European Green Digital Coalition, and partners with NGOs, governments, and institutions to promote digital decarbonization strategies and accelerate net-zero transitions globally.
Measurable Impacts
Cisco has reported strong progress across multiple ESG metrics:
| Category | Metric | Status (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Global electricity from renewable sources | 85% |
| Emissions Reduction | Scope 1 and 2 net zero target | On track for 2025 |
| Circular Product Returns | Returned hardware for reuse/recycling | 47% |
| Product Circularity Compliance | Products meeting circular design standards | 82% |
| Recyclable Packaging | Recyclable or compostable packaging | 97% |
| Digital Skills Access | Individuals trained via Networking Academy | 3.2 million in FY2023 |
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
Despite its leadership, Cisco faces some key challenges:
- Scope 3 emissions: Emissions from the use of sold products represent >70% of Cisco’s total carbon footprint. Reducing these emissions depends heavily on customers upgrading to newer, more efficient products.
- E-waste scaling: Though take-back rates are increasing, achieving a closed-loop hardware cycle at scale remains difficult due to global logistics, customer behavior, and regulatory variations.
- Chip manufacturing emissions: Cisco relies on external suppliers for chips and components, and influencing their emissions requires collaborative supplier initiatives and increased transparency.
Future Plans and Long-Term Goals
Cisco’s forward-looking strategy focuses on scaling digital decarbonization, including:
- Reaching 100% renewable electricity by 2025
- Ensuring circular design in 100% of new products and packaging by FY2025
- Achieving net zero across all scopes by 2040, with verified SBTi targets
- Expanding the Networking Academy to reach 25 million students by 2030
- Driving energy innovation in AI networks, 5G, and edge computing to reduce infrastructure emissions
Comparisons to Industry Competitors
Cisco’s sustainability approach outpaces many of its peers in circular economy leadership and energy efficiency:
| Company | Net Zero Goal | Circular Design Goals | Renewable Energy Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco Systems | 2040 | 100% new products by FY2025 | 85% (target: 100% by 2025) |
| HP Inc. | 2040 | 75% product circularity by 2030 | 58% (2022) |
| Dell Technologies | 2050 | 100% packaging recyclability by 2030 | 59% (2022) |
Cisco’s leadership in product take-back, circular design, and energy-efficient innovation sets it apart. However, like peers, it continues to face challenges in reducing indirect (Scope 3) emissions and managing e-waste across a global customer base.
Our Thoughts
Cisco’s sustainability journey is a strong model of how tech companies can balance digital growth with environmental responsibility. Its forward-leaning policies on circular economy design, transparent emissions targets, and inclusive technology access show a clear alignment with long-term climate goals and social equity. While Scope 3 emissions and e-waste logistics remain difficult challenges, Cisco’s proactive stance and clear benchmarks suggest it will remain a leader in sustainable innovation.






